SUMMARY
- In the midst of the pandemic science is now being widely misunderstood and misrepresented on social media.
- This translates into scepticism, vaccine hesitancy and refusal even for those who in high risk groups who would benefit from it most.
- This post seeks to de-bunk the more common vaccine myths.
The beauty of science:
I have always loved science. As a young boy, looking back, I was clearly a bit of a geek. There can’t have been many 10 year olds swabbing agar dishes enriched with honey and watching with awe the resultant bacterial colonies as they grew. I loved my tiny microscope and the world it revealed almost as much as I loved my bike – both represented freedom from boredom and frustration, and beyond that allowed my mind to settle on something solid and real in an uncertain world.
I learned that though most of my microscopic pets were beneficial, some caused disease and death, and since humans have lived in towns and herded animals, they cause plagues. Up till very recently these have caused immense suffering and without any recourse to control measures other than haphazard restrictions, quarantine and isolation. The walling off of villages, the yellow cross on the nailed in door.
 |
| Fellow travellers |
Plagues have been seen as Gods will, collective punishment for sins, or the devils work. During the terrible course of the Spanish Flu, the best guess was that it was due to a bacteria; completely wrong of course.
Now, thanks to science, we live in an age when we can understand the origin, cause, management, treatment and prevention of plagues. Yet in the face of COVID we flounder as a society in terms of our response. We are also confused by conflicting information leading to misunderstanding and division which an appreciation of what science is telling us should help us avoid.
This plays out in reality – in a YouGov poll, 40% of UK respondents stated that there are undisclosed harmful effects of vaccines and 25% felt that the MRNA vaccines are not safe. Even more sadly, about half thought that the risks of climate change are being over-estimated. Clearly, ‘science’ is not winning as many minds as it might.
Preventing illness by vaccination before it arrives is a modern blessing. So why have 15% of people in the UK offered vaccines not taken up the offer? Why is vaccination hesitancy common throughout the world?
As usual, those missing the vaccine are those most likely to need it the most, members of the BAME community who live in more crowded households in higher impact areas. Vaccine hesitancy may be falling due to the threat of new viral variants, but it remains an issue for those who have not yet made up their minds about the vaccine.
Science under threat
‘Science’ in the public mind is under threat like never before. On-line publishers are free to share more or less whatever pseudo-science they like, claiming the ascendancy of freedom of speech over responsibility.
There have been increasing concerns that such information is damaging to health and can cause real misery for those who are needlessly hit by C19 after vaccine hesitancy, by those whose infections spread to others, as well as the fear and anxiety induced in the mind by the more whacky theorists.
Anti vaccination
Anti-vaccination in not new. There has been a small segment of society actively campaigning against vaccination since our first attempt to prevent and eliminate the misery of smallpox. This was driven by fears of interfering with nature, defying God’s will, a lack of trust in authority and fears of having poorly understood ‘stuff’ injected into the body. For some, these instinct driven fears persist through the centuries.
There are many sources of anti-vaxx misinformation, Mercola’s supplement platform, “Americas Frontline Doctors” come to mind, but there are many others. They issue compelling and powerfully deceptive information enhanced by appeals to emotion. Many are convinced, or confused. The content needs examination to reveal its weaknesses and I suspect much of what it said is taken at face value. Modern snake oil salespeople.
Indeed, they have now been transformed into the mainstream by unedited, unregulated, superficially convincing websites and social media platforms where any opinion can masquerade as good science. Misinformation and disinformation has created its own pandemic of illness and misery and could cause real problems in tacking COVID19, and future pandemics.
Despite the decline in our third wave, there seems no end to the global Sars-Cov2 pandemic. Mutations are arising causing variants which increase the Reproduction number and thus the levels of infection or vaccination needed for herd immunity. Vaccine hesitancy is becoming a bigger dilemma.
Of course, there are many who already hold a strong view, certain that vaccines are not for them, or happy that they are – thats fine. There are others who have a mission to stop vaccination in its tracks – they tend to drive me to distraction, but the information they publish lays bare the myths of anti-vaccination.
So, let’s have a look at what they are:
Myth 1 – “Vaccines are not needed”
 |
| Overloaded hospitals |
Myth 2 – “Vaccines don’t work”
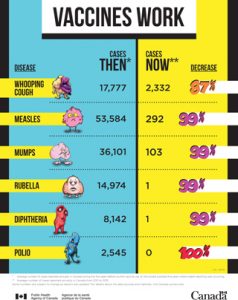 |
| COVID vaccines work too! |
Vaccine trials have shown impressive benefits in terms of reduction of infection, even more impressive data on reductions of severe illness and hospitalisations.
Vaccinations have saved countless lives. It has, for instance, been calculated that the eradication of smallpox has saved 300,000,000 lives as well as the terrible symptoms of the illness and scarring left for survivors.
Similiar calculations of benefit can be made for polio, diptheria, tetanus, rabies, and so many others, but with the absence of those illnesses, and our lack of experience of them, the vaccine side effect become prominent in our culture.
So, just about all the data suggest the vaccines work incredibly well. Vaccines do work. Benefits way exceed the harms.
Myth 3 – “Vaccinations are not natural”
This old arguments has surfaced again. Vaccination is unnatural. This is true, but so are many diseases if you look at it like that. Most of our endemic illnesses have evolved with us and because of us. Most modern diseases are ‘unnatural’. So, Im afraid, is the planet we have changed so much.
For instance, we have millions of nanoparticles of iron in our brains and others in our hearts. These come from air pollution affecting the majority of urban dwellers on the planet. Plastic particles are now found even in otherwise health human placentas. The arguments that vaccines are somehow unnatural is not realistic when we have strayed so far from our natural roots, or any life resembling what could be called natural. We have to live in a very unnatural world, with unnatural illnesses and unnatural treatments.
Myth 4 – “Vaccines cause harm”
With all medical interventions there is a trade off between harm and benefit. The old maxim of “Do no harm” has never been realistic, medicine strives to “do more good than harm”. Vaccines have done harm, there have been problems, allergic reactions, rashes, headaches, and others. Side effects become the real individual experience while absence of disease is not actually experienced in real time by anyone, though of immense benefit.
 |
| Social media that is! |
It is tough when vaccinating millions to avoid the fact that immediately after the vaccination there will be unwanted events. Things will happen, some vaccine related and some just by chance which happen equally in both vaccinated as well as unvaccinated populations. (Such as Autism). If you’ve just had a vaccine, that side effect will stick in the mind and make the news.
Myth 5 – “COVID Vaccines cause Infertility”
Anti-vaxx websites claim vaccines against Sars-Cov2 contain genes for a protein called Synctin1 and will lead to a reaction against naturally occurring Synctin-1 in the human placenta, and so claim this will lead to infertility. Lets leave aside the fact that the vast majority of vaccine recipients are too old for this to be an issue, and the fact that vaccine manufactures acknowledge that care needs to be taken in pregnancy when it comes to vaccines – this is simply due to not enough pregnant women in the trials.
 |
| No problems there |
Concerns about infertility rest on the supposition that enough of the strings of amino acids which make up the spike proteins induced by the vaccine and the placental protein are similar – which they aren’t, or that the shape of the proteins are similar, again which they are not.
Similar nonsensical claims are made that HIV segments are ‘in the vaccine” too. It’s a bit like saying Macbeth and the National Trust handbook are the same thing because they both contain the words “…to a forest…”.
Animal studies early in vaccine development showed that there was no effect on fertility and indeed there is no theoretical reason why there should be. Further reassurance comes from the lack of risk of miscarriage in women who experience infection with a full blown immune reaction to the spike protein, more severe than vaccine induced immunity and without any effect on fertility or miscarriage.
Myth 6 – “Vaccines make the infection worse”
This claim relates to Antibody Dependent Enhancement (ADE). This occurs when the second infection is worse than the first. This happens when the initial infection invokes a weak or partial immune response, or a different strain comes along. When the virus reinfects, these weaker ‘non-neutralising’ antibodies stick to the virus and carry it to immune cells which ingest it, effectively doing the viruses work for it and allowing the virus to replicate once inside the cell, thus worsening the infection.
 |
| Some antibodies are better than others |
This is sometimes the case with Dengue fever, and happened in the failed attempt to create a vaccine against Respiratory Syncytial Virus, a cause of bronchiolitis in small children.
So does it happen in COVID19? The answers seems a resounding no. For one thing, Sars-Cov2 infections target respiratory and other cells rich in ACE2 receptors and not the immune cells needed for ADE to occur. Further, re-infections have so far been very uncommon and when they do occur, are usually milder, not more severe.
That is, the opposite of ADE takes place. It seems that the majority of people infected do generate a significant antibody response which makes the next infection far less severe if noticed at all.
There has been no evidence of ADE in vaccine trials or post market surveillance and it is reasonable to expect that it it were to be a problem, it would have shown up by now. It hasn’t, and ADE as a vaccine side effect is another fear inspiring myth.
Myth 7 – “Vaccines cause autoimmune diseases”
 |
| MS – my Auto-immune disease |
One worry is that COVID19 infection itself can create a longer lasting immune condition as the body could potentially be sensitised against it own ACE2 receptors. This is still an evolving picture and may well apply only to a susceptible sub-group of the population. Long Covid is a real and immediate problem and like other viruses there could be longer term problems we are yet to define. This makes vaccination more, not less appealing.
Fie example, the consensus among MS experts is that COVID19 vaccine is safe and effective in neurology patients, including people with MS and the disease is well worth avoiding. The same applies to other autoimmune conditions but anyone affected by autoimmune disease or having treatment needs to get tailored advice from their specialist teams as timing of treatment of vaccination might need tweaking to get the best immune response.
This is a bit like the infertility myth, parts of the vaccine causing a reaction against our own cells. While there seems no clear evidence that this is the case, it would clearly be a whole lot less of a risk than that posed by the illness itself.
Myth 8 – “The vaccine will change my genes”
This one is easy. The mRNA vaccines simply cannot do this. For them to be able to they would need to change the mRNA to DNA and the vaccine lacks the enzyme tool to enable this to happen.
The vaccine mRNA instructs the cellular machinery to make spike protein and is soon degraded. Not also that permanent insertion of viral DNA into our genome has been common over our evolution, indeed accelerated it.
This is a lie which plays into our emotional understanding of who we are. The idea of having our genome messed about with is a sci-fi horror story, but it is all fiction and no science.
Myth 9 – “Vaccines don’t prevent transmission so why take them?”
Well not so much a myth as something that takes time to prove. The worry is that even those who have been infected or vaccinated can carry the virus in their nose and throat and thus spread the infection before their immune system has time to destroy the viruses.
While hard to prove, it is very reasonable to assume that if you have been previously infected or vaccinated you will eliminate viruses more quickly and thus be less likely to spread the infection less than if you have no immunity at all.
That asymptomatic infections are reduced by 82% the Astra Zeneca vaccine provided more than a hint that it does reduce transmission. That it reduces asymptomatic infections is important as this is a significant means of spread. Reducing it means that reducing transmission is inevitable, but just needs the data to roll in. It has.
Myth 10 – “Vaccines contain microchips”
I thought I’d save this till last as it really is reaching the realms of paranoia. For one thing, microchips are too big to pass thought the needle used to inject vaccines. But beyond the technicalities, if it were true, then surely there would be just one person involved in vaccine design or manufacture prepared to blow the whistle – it would be a huge story after all! There isn’t.
Also, if it were true someone somewhere would have got hold of a vaccine and has a look at it under a commonly available optical microscope and searched for the chip? They haven’t.
Further, all the vaccines come in multi-dose vials containing enough for 10 vaccinations. They are diluted and drawn up into 10 syringes for injecting. How would the unsuspecting nurse ensure that there was one chip in each of the doses? It would be impossible.
That we are all being ‘chipped’ like we microchip our pets is in the realms of complete fantasy. Yet for some the story sticks. It’s more of a lie than a myth.
So what to do??
I could go on, but these are the main issues I have found common to anti vaccination websites and video clips. As time goes by I feel most of them will melt away as the benefits of community immunity grows and the claimed disasters fail to materialise.
My daughter has had the vaccine with the minor side effect of tiredness for a day, my aged neighbours and friends too have had the jab. Anecdote I know, but no problems so far. I keenly await my turn in the queue.
If you want to know more about the detail of the vaccines, please have a look here.
Right now we are, in effect, preparing for a possible next wave and certainly for the next winter when we all hope to avoid another winter like this and enjoy a Festive season without restrictions. (Other that the border restrictions which will be needed to keep out new variants)
For that to happen we have to be able to keep the viral population low enough for outbreaks to be managed by local means. When we get infected, we increase the total number of viruses in the total viral population. We want to reduce that number.
So to be pre-armed with antibodies and T cells ready to destroy the virus before it gets a hold and starts its incredible reproduction is a wonderful thing; for some of us that is infection, but for most it needs vaccination, a real achievement of science, technology and society in a difficult pandemic prone world.
 |
| Christmas 2021??? |


Hi Colin,
Much of what you say I completely agree with; but you haven't mentioned the other side of science, which is the not-at-all benign influence of American big pharma on the previously noble pursuit of knowledge and understanding which you call science. Alas, ever since American doctors were paid to advertise the health-giving effects of smoking, the capitalists have been interfering with science, and influencing people in dubious ways – and they still are. What do you think of this current TV ad?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sLB0MaY7luE
There's big money there, trying to sell an expensive vaccine to medically illiterate people by emotional blackmail. Notice that they don't actually claim anything at all – just a lot of "who knew?"s. That's Trump speak – and I didn't trust him, either…
That's why so many people don't trust "science" nowadays. Because it's been so perverted, and you can't tell who to believe any more.
Dizzy's skeptical thinking link points out that most published papers turn out to be wrong, so you can always find one or two to support any theory. At the end of the day, you have to trust someone else's judgement – but whose?